- What is AraPPISite?
- How to access an interested PPI?
- How to highlight interested residue pairs?
- How to evaluate interested 3D structures of protein complexes?
- How to interact with 3D structures by mouse operations?
- How to download 3D structures of protein complexes?
- How to cite?
What is AraPPIsite?
AraPPISite is a database that presents fine-grained interaction details for 7,336 A.thaliana PPIs, including 27 PPIs with experimental complex structures and 7,309 PPIs whose interaction details are inferred from two distinct computational pipelines as follows.
First, the 3D structures of 3,023 A. thaliana PPIs are modeled by using Homology Modeling of Protein Complex (HMPC) technique or the Protein Interactions by Structural Matching (PRISM) software. Multiple complex structures based on different template complexes could be predicted for a PPI, however, only the one with the highest quality considering the sequence identity and the resolution is displayed in AraPPISite. For each predicted complex structure, AraPPISite not only provides an interactive user interface for browsing the interaction sites in the context of 3D structures, but also lists detailed evolutionary and physicochemical properties (e.g. residue conservation, and estimated energy score) of these sites (Example).
Second, AraPPISite assigns the domain-domain interactions or the domain-motif interactions to 4,286 PPIs whose 3D structures cannot be modeled. In this case, the users can easily query the protein interaction regions at the sequence level (Example).
AraPPISite is a free and user friendly database. It does not require user registration or any configuration on local machines.
How to access an interested PPI?
AraPPISite provides two ways to access an interested PPI.
1. Regular search. Users can enter a pair of protein IDs: TAIR identifier, Uniprot accession number, Gene name and keyword are supported. Start
2. Network-based search. Users can search PPIs with predicted 3D structures. By entering a protein ID (TAIR identifier is supported), users can search PPIs associated with the query protein. Moreover, users can access the interaction site details of the interested PPI. Alternatively, users can also search domain-domain interaction and domain-motif interaction information through the network-based search. Start
An example of searching PPIs with predicted 3D structures:

How to highlight interested residue pairs?
Choose interested residue pairs and click the show button, then the residue pairs will be highlighted on the 3D structure.
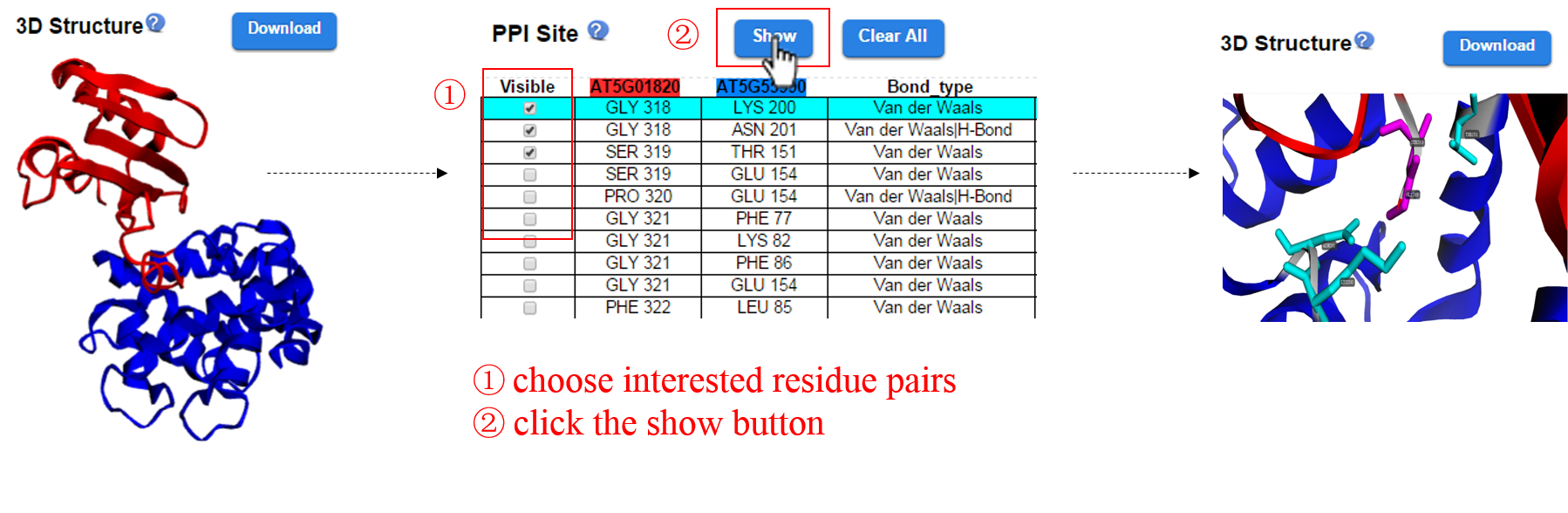
How to evaluate interested 3D structures of protein complexes?
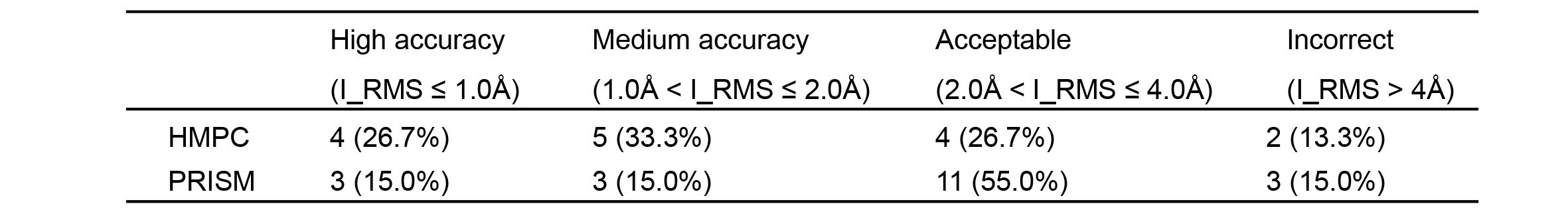
To evaluate the quality of HMPC and PRISM complex structures in AraPPISite, 27 PPIs with experimental complex structures are served as a test set (i.e., golden standard), in which 15 and 20 PPIs can be modeled using HMPC and PRISM respectively.
According to the evaluation criterion of Critical Assessment of Predicted Interactions (CAPRI), which is a community-wide experiment to assess the accuracy of predicted 3D structures of protein complexes, the predicted protein complex structures can be grouped into four categories on the basis of the backbone root-mean-square deviation of interface residues (I_RMS): high accuracy (I_RMS ≤ 1.0Å), medium accuracy (1.0Å < I_RMS ≤ 2.0Å), acceptable (2.0Å < I_RMS ≤ 4.0Å) and incorrect (I_RMS > 4Å). With respect to the 15 complex structures predicted by HMPC, 4 (26.7%) complex structures achieve high accuracy, 13 (86.7%) complex structures are predicted correctly, and 2 (13.3%) complex structures are predicted incorrectly (Table 1). Regarding the 20 complex structures predicted by PRISM, 17 (85.0%) and 3 (15.0%) are predicted correctly and incorrectly, respectively (See the following table). Comparatively, the accuracy of PRISM is inferior to that of HMPC, meaning that more cautions should be taken when dealing with the complex structures as well as the corresponding interaction sites inferred from PRISM.
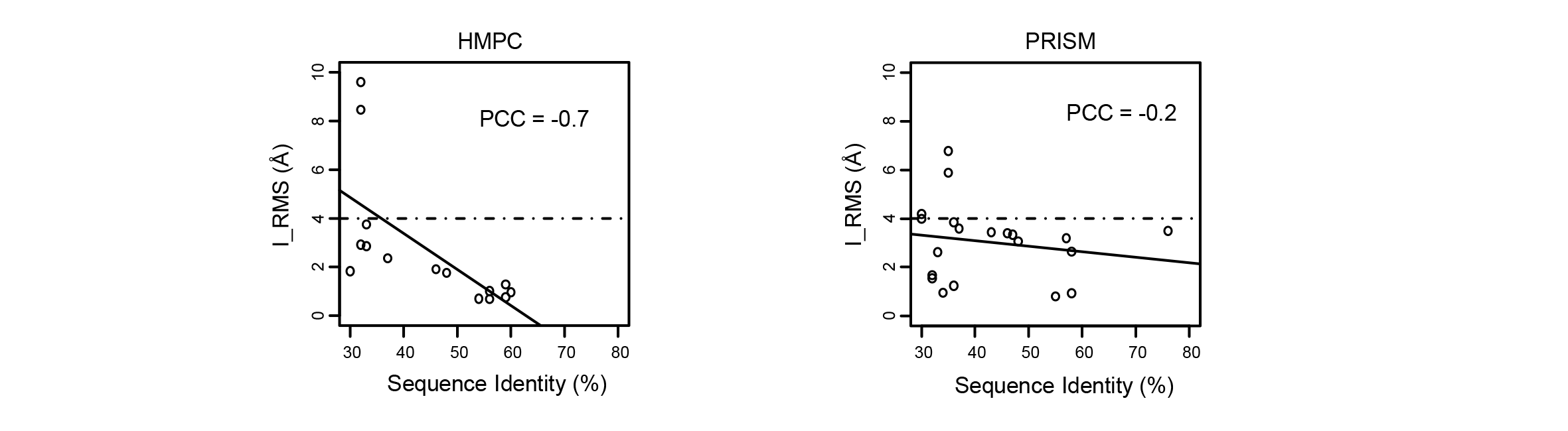
Due to the prediction principle of HMPC, the quality of predicted protein complex structures should be relevant to the sequence identity between interacting proteins and their templates. As expected, among the HMPC-predicted complex structures, the I_RMS values and the sequence identities show a strong negative correlation [Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) = -0.7] (See the following figure). Therefore, a linear regression model (I_RMS = 9.32 - 0.15*sequence identity) is fitted based on the relationship between the I_RMS values and the sequence identities. We classified a HMPC complex structure as high confidence (★★★) when the sequence identity is above 55% (i.e., estimated I_RMS ≤ 1.0Å according to the linear regression model); medium confidence (★★☆) when the sequence identity is from 36% to 55% (i.e., estimated 1.0Å < I_RMS ≤ 4.0Å); and low confidence (★☆☆) when the sequence identity is less than 36% (i.e., estimated I_RMS > 4Å). The confidence of each HMPC complex structure can be obtained when the cursor is placed on the name of complex structures.
However, it is a pity that the correlation between the I_RMS values and the sequence identities in the PRISM complex structures is very weak (PCC = -0.2) (See the following figure), which precludes the reliability estimation of the PRISM complex structures in AraPPISite based on the sequence identities.
How to interact with 3D structures by mouse operations?
Visualization of protein structures is implemented by 3Dmol.js, which is an object-oriented, webGL based JavaScript library for online molecular visualization - No Java required!
| Movement | Mouse Input | Touch Input | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotation | Primary Mouse Button | Single Touch | ||
| Translation | Middle Mouse Button or Ctrl+Primary | Triple Touch | ||
| Zoom | Scroll Wheel or Second Mouse Button or Shift+Primary | Pinch (double touch) | ||
| Slab | Ctrl+Second | Not Available |
How to download 3D structures of protein complexes?
Users can download the pdb file of interested protein structure by clicking the download button in the result page. Alternatively, AraPPISite allows the users to download all of the data for further analyses in the download page.
How to cite?
Hong Li, Shiping Yang, Chuan Wang, Yuan Zhou, and Ziding Zhang. (2015) AraPPISite: a database of fine-grained protein-protein interaction site annotations for Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Molecular Biology.
